
Discussion Post Perfection: Expert Guidance for Accounting
30. Managerial accounting: A) is more future oriented than financial accounting. B) tends to...
Managerial accounting:
A) is more future oriented than financial accounting.
B) tends to summarize information more than financial accounting
C) is primarily concerned with providing information to external users.
D) is more concerned with precision than timeliness.
31. The annualized discount rate on a particular money market instrument, is 3.75%. The face value is...
1. The price of $8,000 face value commercial paper is $7,930. If the annualized discount rate is 4%, when will the paper mature? If the annualized investment rate % is 4%, when will the paper mature?
2. How much would you pay for a Treasury bill that matures in one year and pays $10,000 if you require a 3% discount rate?
3. The annualized discount rate on a particular money market instrument, is 3.75%. The face value is $200,000, and it matures in 51 days. What is its price? What would be the price if it had 71 days to maturity?
32. Connor Company's budgeted prices for direct materials, direct manufacturing labor, and direct...
Flexible Budget
Connor Company's budgeted prices for direct materials, direct manufacturing labor, and direct marketing (distribution) labor per attache case are $40, $8, $12, respectively. The president is pleased with the following performance report.
Actual Costs | Static Budget | Variance | |
Direct materials | 364,000 | 400,000 | 36,000 F |
Direct manufacturing labor | 78,000 | 80,000 | 2,000 F |
Direct marketing (distribution)labor | 110,000 | 120,000 | 10,000 F |
48,000 F
Actual output was 8,800 attache cases. Assume all three direct-cost items above are variable costs.
Is the president's pleasure justified? Prepare revised performance report that uses flexible budget and a static budget.
33. Exercise 7-6 (Part Level Submission) Jobs, Inc. has recently started the manufacture of Tri-Robo,...
Exercise 7-6 (Part Level Submission) Jobs, Inc. has recently started the manufacture of Tri-Robo, a three-wheeled robot that can scan a home for fires and gas leaks and then transmit this information to a smartphone. The cost structure to manufacture 20,900 obos is as follows. Cost Direct materials ($52 per robot) $1,086,800 877,800 Direct labor ($42 per robot) Variable overhead ($7 per robot) 146,300 Allocated fixed overhead ($29 per robot) 600,000 Total $2,710,900 Jobs is approached by Tienh Inc., which offers to make Tri-Robo for $119 per unit or $2,487,100 Following are independent assumptions
34. 1 In Ratio Analysis, the term Capital Employed refers to: (a)Equity Share Capital,(b)Net worth,(c)Sh
1 In Ratio Analysis, the term Capital Employed refers to:
(a)Equity Share Capital,(b)Net worth,(c)Shareholders’ Funds,(d)None of the above
2 Dividend Payout Ratio is:
(a)PAT Capital, (b)DPS ÷ EPS,(c) Pref Dividend ÷ PAT, (d) Pref Dividend ÷ Equity Dividend
3 DU PONT Analysis deals with:
(a) Analysis of Current Assets, (b)Analysis of Profit, (c)Capital Budgeting, (d) Analysis of Fixed Assets
35. The Bihar Coal Company Limited are lessee of a mine on a royalty of 50 paise per ton of coal...
The Bihar Coal Company Limited are lessee of a mine on a royalty of 50 paise per ton of coal raised, with a dead rent of Rs.30,000 per annum, and power to recoup shortworkings during the first five years of the lease. The output for the first three years was as follows: 1st Year 15,000 tons; 2nd year 50,000 tons; 3rd year 75,000 tons. Draft the necessary journal entries in the books of both parties. You are also required to write up Minimum Rent account, Royalties Account, Shortworkings Account, Landlord’s Account and Profit and Loss Account
36. Describe the roles and the basic relationships among the major parties in a...
Describe the roles and the basic relationships among the major parties in a corporation—stockholders, board of directors, and managers. How are corporate owners rewarded for the risks they take?
Describe the roles and the basic relationships among the major
37. Question Which of the following best describes the activities of the accounting function? a....
Question
Which of the following best describes the activities of the accounting function?
a. inventory control, accounts payable, fixed assets, and payroll
b. fixed assets, accounts payable, cash disbursements, and cost accounting
c. purchasing, cash receipts, accounts payable, cash disbursements, and payroll
d. inventory control, cash receipts, accounts payable, cash disbursements, and payroll
e. inventory control, cost accounting, accounts payable, cash disbursements, and payroll
38. 1. Carlita began 2004 with a taxes payable account balance of $3,000. O
1. Carlita began 2004 with a taxes payable account balance of $3,000. On December 31, 2004, its taxes payable account balance is $7,000. How much did Carlita pay to the tax authorities during the year?
$2,000
$6,000
$4,000
Cannot be calculated
2. On January 1, 2005, Jon Sports has a bond payable of $200,000. During 2005, it pays off $20,000 of the outstanding bond principal and issues a new $70,000 bond. There are no other transactions related to the bond payable account.
What is Jon Sports' December 31, 2005 bond payable balance?
A debit balance of $250,000
A credit balance of $150,000
A debit balance of $150,000
A credit balance of $250,000
3. The next 7 questions are based on Panjim Trading Company's cash T-account for 2005.
Based on Panjim's 2005 cash T-account, which one of the following statements must be true?
During 2005, Panjim's total merchandise sales were $60,000
During 2005, Panjim's total merchandise purchases were $44,000
During 2005, Panjim issued $75,000 of debt
Panjim did not record any tax expense for 2005
4. Panjim began 2005 with salaries payable balance of $75,000. It had 2005 salary expense of $80,000. Its 2005 ending salaries payable balance must be:
$95,000
$55,000
$155,000
$105,000
39. The following selected transactions were completed during August between Summit Company and...
PR 5-4A Sales-related and purchase-related transactions for seller and buyer
The following selected transactions were completed during August between Summit Company and Beartooth Co.:
Aug. 1. Summit Company sold merchandise on account to Beartooth Co., $48,000, terms FOB destination, 2/15, n/eom. The cost of the merchandise sold was $28,800.
2. Summit Company paid freight of $1,150 for delivery of merchandise sold to Beartooth Co. on August 1.
5. Summit Company sold merchandise on account to Beartooth Co., $66,000, terms FOB shipping point, n/eom. The cost of the merchandise sold was $40,000.
6. Beartooth Co. returned $10,500 of merchandise purchased on account on August 1 from Summit Company. The cost of the merchandise returned was $6,300.
9. Bear tooth Co. paid freight of $2,300 on August 5 purchase from Summit Company.
15. Summit Company sold merchandise on account to Bear tooth Co., $58,700, terms FOB shipping point, 1/10, n/30. Summit Company paid freight of $1,675, which was added to the invoice. The cost of the merchandise sold was $35,000.
16. Bear tooth Co. paid Summit Company for purchase of August 1, less discount and less return of August 6.
25. Bear tooth Co. paid Summit Company on account for purchase of August 15, less discount.
31. Bear tooth Co. paid Summit Company on account for purchase of August 5.
Instructions
Journalize the August transactions for (1) Summit Company and (2) Bear tooth Co.
40. Technovia Inc. has two divisions: Auxiliary Components and Audio
Technovia Inc. has two divisions: Auxiliary Components and Audio Systems. Divisional managers are encouraged to maximize ROI and EVA. Managers are essentially free to determine whether goods will be transferred internally and what will be the internal transfer prices. Headquarters has directed that all internal prices be expressed on a full cost-plus basis. The markup in the full cost pricing arrangement, however, is left to the discretion of the divisional managers. Recently, the two divisional managers met to discuss a pricing agreement for a subwoofer that would be sold with a personal computer system. Production of the subwoofers is at capacity. Subwoofers can be sold for $31 to outside customers. The Audio Systems Division can also buy the subwoofer from external sources for the same price; however, the manager of this division is hoping to obtain a price concession by buying internally. The full cost of manufacturing the subwoofer is $20. If the manager of the Auxiliary Components Division sells the subwoofer internally, $5 of selling and distribution costs can be avoided. The volume of business would be 250,000 units per year, which is well within the capacity of the producing division. After some discussion, the two managers agreed on a full cost-plus pricing scheme that would be reviewed annually. Any increase in the outside selling price would be added to the transfer price by simply increasing the markup by an appropriate amount. Any major changes in the factors that led to the agreement could initiate a new round of negotiation; otherwise, the full cost-plus arrangement would continue in force for subsequent years.
Required:
1. Calculate the minimum and maximum transfer prices.
2. Assume that the transfer price agreed on between the two managers is halfway between the minimum and maximum transfer prices. Calculate this transfer price. What markup over full cost is implied by this transfer price?
3. Refer to Requirement 2. Assume that in the following year, the outside price of subwoofers increases to $32. What is the new full cost-plus transfer price?
4. Assume that two years after the initial agreement, the market for subwoofers has softened considerably, causing excess capacity for the Auxiliary Components Division. Would you expect a renegotiation of the full cost-plus pricing arrangement for the coming year? Explain.
41. In 20-- the annual salaries paid each of the officers of Abrew, Inc., follow. The officers are...
In 20-- the annual salaries paid each of the officers of Abrew, Inc., follow. The officers are paid semimonthly on the 15th and the last day of the month. Compute the FICA taxes to be withheld from each officer's pay on (a) November and (b) December 31
42. If total assets increased $20,000 during a period and total liabilities increased $12,000 during the...
If total assets increased $20,000 during a period and total liabilities increased $12,000 during the same period, the amount and direction (increase or decrease) of the change in owner’s equity for that period is a(n):
A. $32,000 increase.
B. $32,000 decrease.
C. $8,000 increase.
D. $8,000 decrease.
43. Barney, Inc., is subject to a 40% income tax rate the following data pertain to the period ended ...
Barney, Inc., is subject to a 40% income tax rate the following data pertain to the period ended when the company produced and sold 45,000 units Sales revenue $1, 350,000 Variable costs 810,000 Fixed costs 432,000 How many units must Barney sell to earn an after-tax profit of $1 80,000? (Show computations)
44. 1. The one-year P6,000 insurance paid was effective December 1. 2. Office rental of P4,000 for...
1. The one-year P6,000 insurance paid was effective December 1. 2. Office rental of P4,000 for the month of December was still unpaid. 3. Interest of 18% per annum on the P60,000 bank loan granted on December 11, has accrued. 4. Advertising placement of P3,600 for three months was effective on December 1 5. Fees of P5,000 collected in advance on December 30 will be for services to be rendered next year. 6. Office supplies unused at the end of the month amounted to P1,600. 7. Furniture and Equipment are estimated to have a useful life of ten years. It was decided to provide depreciation for December
45. Maria has an annual contract with morneau insurance company to provide property maintenance...
Maria has an annual contract with morneau insurance company to provide property maintenance services; this includes lawn care, snow removal and parking lot maintenance. maria spends, on average, 20 hours per week working at the company’s premises and is paid a flat amount monthly. she hires part-time workers, when necessary, to assist her. maria does not have any other clients. maria uses her own small tools; however the company supplies and maintains a riding lawn mower and a snow plow for her use. her contact at the company is paul lane, the facilities manager, who meets with her every monday to discuss the work to be done that week. paul approves maria’s monthly invoices and submits them to accounts payable. does maria have a contract of service or a contract for service with morneau insurance company? as the company’s payroll manager, explain to paul the process and factors you used to make your decision.
46. Vat Company acquired a 30 percent interest in the voting
Vat Company acquired a 30 percent interest in the voting stock of Zel Company for $331,000 on January 1, 2011, when Zel’s stockholders’ equity consisted of capital stock of $600,000 and retained earnings of $400,000. At the time of Vat’s investment, Zel’s assets and liabilities were recorded at their fair values, except for inventories that were undervalued by $30,000 and a building with a 10-year remaining useful life that was overvalued by $60,000. Zel has income for 2011 of $100,000 and pays dividends of $50,000. Assume undervalued inventories are sold in 2011.
REQUIRED
1. Compute Vat’s income from Zel for 2011.
2. What is the balance of Vat’s Investment in Zel account at December 31, 2011?
3. What is Vat’s share of Zel’s recorded net assets at December 31, 2011?
47. Test - Tax Specialist Certification Test (2018) Form 1040 A taxpayer is required to tle Form 1040...
Test - Tax Specialist Certification Test (2018) Form 1040 A taxpayer is required to tle Form 1040 when they elaim which of the tollowing adjustments to i.ome? 。Budent loan merest deduction 。Haam savrgs account don. O Tradtonal IRA contribution deduction O Educator expenses Mark for folow up Question 2 of 7s. A taxpayer should include which of the following when figuring their federal gross income O Pricr-year federal income tax refund O Ordinary dividends O Personal injury compensation O Qualified disaster relief payments Mark for follow up Question 3 of 75 Which of the following taxpayers may not be able to claim full benefits for some common itemized deductions? O Andre, a single taxpayer whose adjusted gross income was $270,000 O Dianne, whose adjusted gross income was $150,000 and will file married tling separately 。Jan and Susan, who are married and fie ajont reun. Ther adjusted gross income was S3 10,000. O Taya, whose adjusted gross income was $280,000. She has a dependent daughter and Sles head of household L Mark for folow up Question 4 of 75 Which of the following situations could prevent a taxpayer from receiving a refund to which they are otherwise entitled? O Fling a return for a tax year for which the statute of limitations has not yet expired O Fling a return for a tax year for which the statute of limitations has expired. O Amending a return two years after the tax was paid, f paid after the fing date.
48. 1. Matheson Electronics has just developed a new electronic device that it believes will have bro...
1. Matheson Electronics has just developed a new electronic device that it believes will have broad market appeal. The company has performed marketing and cost studies that revealed the following information:
a. New equipment would have to be acquired to produce the device. The equipment would cost $486,000 and have a six-year useful life. After six years, it would have a salvage value of about $24,000.
b. Sales in units over the next six years are projected to be as follows: Year Sales in Units 1 18,000 2 23,000 3 25,000 4–6 27,000
c. Production and sales of the device would require working capital of $63,000 to finance accounts receivable, inventories, and day-to-day cash needs. This working capital would be released at the end of the project’s life.
d. The devices would sell for $35 each; variable costs for production, administration, and sales would be $20 per unit.
e. Fixed costs for salaries, maintenance, property taxes, insurance, and straight-line depreciation on the equipment would total $159,000 per year. (Depreciation is based on cost less salvage value.)
f. To gain rapid entry into the market, the company would have to advertise heavily. The advertising program would be: Year Amount of Yearly Advertising 1–2 $ 92,000 3 $ 72,000 4–6 $ 62,000
g. The company’s required rate of return is 18%. Click here to view Exhibit 11B-1 and Exhibit 11B-2, to determine the appropriate discount factor(s) using tables. Required: 1. Compute the net cash inflow (cash receipts less yearly cash operating expenses) anticipated from sale of the device for each year over the next six years.
2-a. Using the data computed in (1) above and other data provided in the problem, determine the net present value of the proposed investment. (Any cash outflows should be indicated by a minus sign. Round discount factor(s) to 3 decimal places.)
2-b. Would you recommend that Matheson accept the device as a new product? Yes No
49. A River Hawk Expeditions provides guided tours in scenic mountainous areas. After the first 11...
A River Hawk Expeditions provides guided tours in scenic mountainous areas. After the first 11
months of operations in 2018, River Hawk has the following account balances.
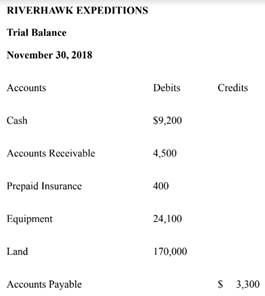
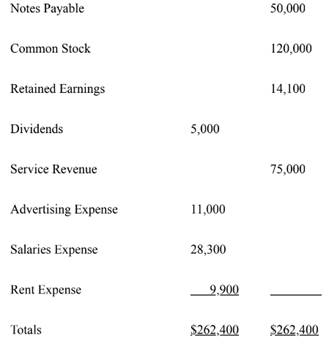
The following transactions occur during December 2018:


Required:
1. Record each transaction.
2. Post each transaction to the appropriate T-accounts.
3. Calculate the balance of each account at December 31.
At December 31, 2019, the trial balance of Darby Company contained the following amounts before adjustment. ______________________________________Debit Credit Accounts Receivable..............................$385,000 Allowance for Doubtful Accounts...............................$ 1,000 Sales Revenue......................................................970,000 Instructions (a) Based on the information given, which method of accounting for bad debts is Darby Company using-the direct write-off method or the allowance method? How can you tell? (b) Prepare the adjusting entry at December 31, 2019, for bad debt expense, assuming an aging schedule indicates that $11,750 of accounts receivable will be uncollectible. (c) Repeat part (b) assuming that instead of a credit balance there is a $1,000 debit balance in Allowance for Doubtful Accounts. (d) During the next month, January 2020, a $3,000 account receivable is written off as uncollectible. Prepare the journal entry to record the write-off. (e) Repeat part (d) assuming that Darby uses the direct write-off method instead of the allowance method in accounting for uncollectible accounts receivable. (f) What type of account is Allowance for Doubtful Accounts? How does it affect how accounts receivable is reported on the balance sheet at the end of the accounting period?