
ofessional Support for Research Papers and Accounting Module
42. “Blast it!” said David Wilson, president of Teledex Company. “We’ve just lost the bid on ...
“Blast it!” said David Wilson, president of Teledex Company. “We’ve just lost the bid on the Koopers job by $4,000. It seems we’re either too high to get the job or too low to make any money on half the jobs we bid.” |
Teledex Company manufactures products to customers’ specifications and operates a job order costing system. Manufacturing overhead cost is applied to jobs on the basis of direct labor cost. The following estimates were made at the beginning of the year: |
Department | ||||||||
Fabricating | Machining | Assembly | Total Plant | |||||
Direct labor | $ | 216,000 | $ | 108,000 | $ | 324,000 | $ | 648,000 |
Manufacturing overhead | $ | 378,000 | $ | 432,000 | $ | 97,200 | $ | 907,200 |
Jobs require varying amounts of work in the three departments. The Koopers job, for example, |
Department | ||||||||
Fabricating | Machining | Assembly | Total Plant | |||||
Direct materials | $ | 4,600 | $ | 200 | $ | 3,000 | $ | 7,800 |
Direct labor | $ | 6,000 | $ | 500 | $ | 7,800 | $ | 14,300 |
Manufacturing overhead | ? | ? | ? | ? | ||||
The company uses a plantwide overhead rate to apply manufacturing overhead cost to jobs. |
Required: | |
1. | Assuming use of a plantwide overhead rate: |
a. | Compute the rate for the current year. |
b. | Determine the amount of manufacturing overhead cost that would have been applied to |
2. | Suppose that instead of using a plantwide overhead rate, the company had used a separate predetermined overhead rate in each department. Under these conditions: |
a. | Compute the rate for each department for the current year. |
b. | Determine the amount of manufacturing overhead cost that would have been applied to |
4. | Assume that it is customary in the industry to bid jobs at 150% of total manufacturing cost (direct materials, direct labor, and applied overhead). |
a. | What was the company's bid price on the Koopers job if a plantwide overhead rate had been used to apply overhead cost? |
b. | What would the bid price have been if departmental overhead rates had been used to apply overhead cost? |
5. | At the end of the year, the company assembled the following actual cost data relating to all jobs worked on during the year. |
Department |
| |||||||
Fabricating | Machining | Assembly | Total plant | |||||
Direct materials | $ | 206,000 | $ | 17,600 | $ | 130,000 | $ | 353,600 |
Direct labor | 226,000 | 124,000 | 278,000 | 628,000 | ||||
Manufacturing overhead | $ | 389,000 | $ | 468,000 | $ | 86,500 | $ | 943,500 |
a. | Compute the underapplied or overapplied overhead for the year, assuming that a plantwide overhead rate is used. |
b. | Compute the underapplied or overapplied overhead for the year, assuming that departmental overhead rates are used. (Enter overapplied overhead costs as negative amounts and underapplied overhead costs as positive amounts.) |
43. Which of the following statements correctly describes the term conversion costs? the cost to con...
Which of the following statements correctly describes the term conversion costs? the cost to convert finished goods to sales to customers the cost of direct materials, direct labor, and manufacturing overhead costs incurred during production the cost of direct labor combined with manufacturing overhead the cost incurred for direct and indirect materials during production
44. 61. A decrease in net assets arising from peripheral or incidental transactions is called a(n)...
61. A decrease in net assets arising from peripheral or incidental transactions is called a(n)
a.capital expenditure.
b.cost.
c.loss.
d.expense.
62. One of the elements of financial statements is comprehensive income. As described in Statement of Financial Accounting Concepts No. 6, "Elements of Financial Statements," comprehensive income is equal to
a.revenues minus expenses plus gains minus losses.
b.revenues minus expenses plus gains minus losses plus investments by owners minus distributions to owners.
c.revenues minus expenses plus gains minus losses plus investments by owners minus distributions to owners plus assets minus liabilities.
d.none of these.
63. Which of the following elements of financial statements is not a component of compre-hensive income?
a.Revenues
b.Distributions to owners
c.Losses
d.Expenses
P64.Which of the following is false with regard to the element "comprehensive income"?
a.It is more inclusive than the traditional notion of net income.
b.It includes net income and all other changes in equity exclusive of owners' invest-ments and distributions to owners.
c.This concept is not yet being applied in practice.
d.It excludes prior period adjustments (transactions that relate to previous periods, such as corrections of errors).
S65.According to the FASB conceptual framework, earnings
a.are the same as comprehensive income.
b.exclude certain gains and losses that are included in comprehensive income.
c.include certain gains and losses that are excluded from comprehensive income.
d.include certain losses that are excluded from comprehensive income.
S66.According to the FASB Conceptual Framework, the elements?assets, liabilities, and equity?describe amounts of resources and claims to resources at/during a
Moment in Time Period of Time
a. YesNo
b. YesYes
c. NoYes
d. NoNo
67. Which of the following is not a basic element of financial statements?
a.Assets.
b.Balance sheet.
c.Losses.
d.Revenue.
68. Which of the following basic elements of financial statements is more associated with the balance sheet than the income statement?
a.Equity.
b.Revenue.
c.Gains.
d.Expenses.
69. Issuance of common stock for cash affects which basic element of financial statements?
a.Revenues.
b.Losses.
c.Liabilities.
d.Equity.
70. Which basic element of financial statements arises from peripheral or incidental transactions?
a.Assets.
b.Liabilities.
c.Gains.
d.Expenses.
COMPREHENSIVE/SPREADSHEET PROBLEM
RATIO ANALYSIS The Corrigan Corporation’s 2007 and 2008 financial statements follow, along with some industry average ratios.
a. Assess Corrigan’s liquidity position and determine how it compares with peers and how the liquidity position has changed over time.
b. Assess Corrigan’s asset management position and determine how it compares with peers and how its asset management efficiency has changed over time.
c. Assess Corrigan’s debt management position and determine how it compares with peers and how its debt management has changed over time.
d. Assess Corrigan’s profitability ratios and determine how they compare with peers and how its profitability position has changed over time.
e. Assess Corrigan’s market value ratios and determine how its valuation compares with peers and how it has changed over time.
f. Calculate Corrigan’s ROE as well as the industry average ROE using the DuPont equation. From this analysis, how does Corrigan’s financial position compare with the industry average numbers?
g. What do you think would happen to its ratios if the company initiated cost-cutting measures that allowed it to hold lower levels of inventory and substantially decreased the cost of goods sold? No calculations are necessary. Think about which ratios would be affected by changes in these two accounts.
Corrigan Corporation: Balance Sheets as of December 31 | ||
|
| 2007 |
Cash | $72,000 | $65,000 |
Accounts receivable | 439,000 | 328,000 |
Inventories | 894,000 | 813,000 |
Total current assets | $1,405,000 | $1,206,000 |
Land and building | $238,000.00 | 271,000 |
Machinery | 132,000 | 133,000 |
Other fixed assets | $61,000.00 | 57,000 |
Total assets | $1,836,000 | $1,667,000 |
|
|
|
Accounts and notes payable | 432,000 | $409,500 |
Accrued liabilities | $170,000.00 | 162,000 |
Total current liabilities | 602,000 | $571,500 |
Long-term debt | $404,290.00 | 258,898 |
Common stock | 575,000 | 575,000 |
Retained earnings | $254,710.00 | 261,602 |
Total liabilities and equity | $1,836,000 | $1,667,000 |
Corrigan Corporation: Income Statements for Years Ending December 31 | ||
| 2008 | 2007 |
Sales | $4,240,000 | $3,635,000 |
Cost of goods sold | 3,680,000 | 2,980,000 |
Gross operating profit | $560,000 | $655,000 |
General administrative and selling expenses | 236,320 | 213,550 |
Depreciation | 159,000 | 154,500 |
Miscellaneous | 134,000 | 127,000 |
Earnings before taxes (EBT) | $30,680 | $159,950 |
Taxes (40%) | 12,272 | 63,980 |
Net income | $18,408 | $95,970 |
Per-Share Data | ||
| 2008 | 2007 |
EPS | $1 | $4 |
Cash dividends | 1 | 1 |
Market price (average) | $12 | $24 |
P/E ratio | 15.4× | 5.65× |
Number of shares outstanding | 23,000 | 23,000 |
46. Micado Corporation was formed on January 1, 2017. At December 31, 2017, Miko Liu, the president...
Micado Corporation was formed on January 1, 2017. At December 31, 2017, Miko Liu, the president and sole stockholder, decided to prepare a balance sheet, which appeared as follows.
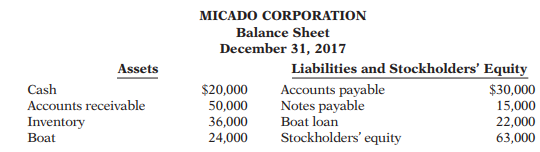
Miko willingly admits that she is not an accountant by training. She is concerned that her balance sheet might not be correct. She has provided you with the following additional information.
1. The boat actually belongs to Miko, not to Micado Corporation. However, because she thinks she might take customers out on the boat occasionally, she decided to list it as an asset of the company. To be consistent, she also listed as a liability of the corporation her personal loan that she took out at the bank to buy the boat.
2. The inventory was originally purchased for $25,000, but due to a surge in demand Miko now thinks she could sell it for $36,000. She thought it would be best to record it at $36,000
3. Included in the accounts receivable balance is $10,000 that Miko loaned to her brother 5 years ago. Miko included this in the receivables of Micado Corporation so she wouldn’t forget that her brother owes her money.
Instructions
(a) Comment on the proper accounting treatment of the three items above.
(b) Provide a corrected balance sheet for Micado Corporation.
47. 41 years 5' 3? 155 pounds Name: Carolyn Cross Age: 41 years Sex: F Height: 5' 3? Weight: 155 pounds
41 years
5′ 3″
155 pounds
Name: Carolyn Cross
Age: 41 years
Sex: F
Height: 5′ 3″
Weight: 155 pounds (BMI 275)
Temperature: 984 F (oral)
Pulse: 76 bpm – regular
Blood pressure: 134/74 mmHg122/72 upon standing
Respiratory rate: 16 bpm
SpO2: 98% on room air
Carolyn Cross
Chief complaint:
Well-woman evaluation
SOAP Note and Differential Diagnoses for iHuman Case
Use this week’s iHuman case titled “Carolyn Cross V2VE” and create a SOAP note with a treatment plan (located at the bottom of the SOAP note
- Provide a subjective, objective, assessment, and plan (SOAP) note on this patient and your treatment plan using the SOAP note template provided Remember to keep the patient’s identity private; use the minimal amount of information possible to get the idea across
- Provide a reference for your treatment plan (in APA format) The reference may come from a journal, a book, etc
- Cite all sources using APA format
- Include three differential diagnoses and support your diagnoses with supporting literature
Skin: | Warm, dry |
Ms Cross is a healthy 41-year-old G2P2 Hispanic-American female who presents for a well-woman examination She has no active medical complaints, but is concerned about her risk of breast cancer as both her mother (age 63) and maternal first cousin (age 44) have been recently diagnosed with intraductal breast cancer Additional risk factors include menarche age 105; first pregnancy age 33; she breast fed each of her two infants for only four months each The patient, reports a normal baseline mammogram at age 40, (report not available) and a history of fibrocystic breast disease She is overweight (BMI 275) with a FH of hypertension, hyperlipidemia (father) and type 2 diabetes (mother)
She is concerned about her risk for breast cancer and does this fact increase her risk of breast cancer, her mother at 63 years old and first cousin 44 year old was recently diagnosed with breast cancer She performs self-breast examines, no lumps or bumps or discharged noted by patient She reports breast tenderness around her menstrual cycle Denies any health problems past or present Immunizations are up to date She gardens and does house work for exercise She reports later she takes vitamin E for fibro cystic breast disease, she had a mammogram 18 months ago Father has hyperlipidemia and HTN and mother is a type 2 DM and just diagnosed at 63 with breast cancer Pt has a glass of wine every night with supper her diet is traditional Hispanic diet Both breast is irregular lump and bump bilateral with slight diffuse tenderness She has two boys and a husband no reported siblings
labs
Name | Value | Units | Reference Range |
Cholesterol | 239 | mg/dL | low risk 239 |
High-density lipoprotein (HDL) | 45 | mg/dL | maj risk 59 |
Low-density lipoprotein (LDL) | 159 | units/L | low risk 159 |
Triglycerides | 40 | mg/dL | (?) 35-135, (?) 40-16 |
Name | Value | Units | Reference Range |
Glucose, 8 hour fasting | 122 | mg/dL |
Name | Value | Units | Reference Range |
Hemoglobin A1c | 64 | % | normal 4-56, elevated risk 57-64, diabetes >67 |
Her papsmear was normal
48. The balance sheet provides a snapshot of the financial condition of a company. Investors and anal...
The balance sheet provides a snapshot of the financial condition of a company. Investors and analysts use the information given on the balance sheet and other financial statements to make several interpretations regarding the company's financial condition and performance Cute Camel Woodcraft Company is a hypothetical company. Suppose it has the following balance sheet items reported at the end of its first year of operation. For the second year, some parts are still incomplete. Use the information given to complete the balance sheet. Cute Camel Woodcraft Company Balance Sheet for Year Ending December 31 (Millions of Dollars) Year 2 Year 1 Year 1 Year 2 Uabiitles and equity Current liabilities: Current assets Cash and equivalents $1,107 Accounts payable $0 $0 405 Accruals Accounts receivable 399 1,188 Notes payable 375 1,485 Inventories $2,700 Total current liabilities $3,375 Total current assets 1,406 Long-term debt 1,125 Net fixed assets Net plant and equipment $3,300 Total debt $1,875 $1,500 Common equity: Common stock 1,575 Retained earnings $5,625 $4,500 Total common equity $6,000 $6,000 Total liabilities and equity $7,500 $7,500 Total assets
49. Roy Akins was the accounting manager at Zelco, Inc., a
Roy Akins was the accounting manager at Zelco, Inc., a tire manufacturer, and he played golf with Hugh Stallings, the CEO, who was something of a celebrity in the community. The CEO stood to earn a substantial bonus if Zelco increased net income by year-end. Roy was eager to get into Hugh’s elite social circle; he boasted to Hugh that he knew some accounting tricks that could increase company income by simply revising a few journal entries for rental payments on storage units. At the end of the year, Roy changed the debits from ?orent expense?? to ?oprepaid rent?? on several entries. Later, Hugh got his bonus, and the deviations were never discovered.
Requirements
1. How did the change in the journal entries affect the net income of the company at year-end?
2. Who gained and who lost as a result of these actions?
50. Dittman's Variety Store is completing the accounting process for the current year just ended, Dec...
Dittman's Variety Store is completing the accounting process for the current year just ended, December 31. The transactions during year have been journalized and posted. The following data with respect to adjusting entries are available: Wages earned by employees during December, unpaid and unrecorded at December 31, amounted to $4, 600. The last payroll was December 28; the next payroll will be January 6. Office supplies on hand at January 1 of the current year totaled $830. Office supplies purchased and debited to Office Supplies during the year amounted to $1, 070. The year-end count showed $465 of supplies on hand. One-fourth of the basement space is rented to Herald's Specialty Shop for $750 per month, payable monthly. At the end of the current year, the rent for November and December had not been collected or recorded. Collection is expected in January of the next year. The store used delivery equipment all year that cost $79, 500; $21, 600 was the estimated annual depreciation. On July 1 of the current year, a two-year insurance premium amounting to $3, 540 was paid in cash and debited in full to Prepaid Insurance. Coverage began on July 1 of the current year. The remaining basement of the store is rented for $1, 980 per month to another merchant. M. Carlos, Inc. Carlos sells compatible, but not competitive, merchandise. On November 1 of the current year, the store collected six months' rent in the amount of $11, 880 in advance from Carlos; it was credited in full to Unearned Rent Revenue when collected. Dittman's Variety Store operates a repair shop to meet its own needs. The shop also does repairs for M. Carlos. At the end of the current year, Carlos had not paid $1, 180 for completed repairs. This amount has not yet been recorded as Repair Shop Revenue. Collection is expected during January of next year. Required: For each of the transactions above, indicate the amount and direction of effects of the adjusting entry on the elements of the balance sheet and income statement. Using the table below, indicate + for increase and - for decrease.