
Achieve Distinction: Professional Help with Accounting Exam
22. Which of the following account is affected from the Drawings of cash in sole- proprietorship busines
Which of the following account is affected from the Drawings of cash in sole- proprietorship business?A) Capital accountB) Shareholder accountC) Liability accountD) Expense account
23. Which of the following is not a component of the balanced scorecard?
Which of the following is not a component of the balanced scorecard?
- Strategic objectives.
- Targets.
- Strategy initiatives.
- Assessment of human resources.
24. Exercise 16-6 Weighted average: Cost per EUP and costs assigned to output LO C2 The Fields Compan...
Exercise 16-6 Weighted average: Cost per EUP and costs assigned to output LO C2
The Fields Company has two manufacturing departments, forming and painting. The company uses the weighted-average method of process costing. At the beginning of the month, the forming department has 25,000 units in inventory, 60% complete as to materials and 40% complete as to conversion costs. The beginning inventory cost of $60,100 consisted of $44,800 of direct material costs and $15,300 of conversion cost.
During the month, the forming department started 300,000 units. At the end of the month, the forming department had 30,000 units in ending inventory, 80% complete as to materials and 30% complete as to conversion. Units completed in the forming department are transferred to the painting department.
Cost information for the forming department is as follows:
25. 71.Under variable costing, which of the following costs would not be included in finished goods...
71.Under variable costing, which of the following costs would notbe included in finished goods inventory?
a.direct labor cost
b.direct materials cost
c.variable factory overhead cost
d.fixed factory overhead cost
72.Under variable costing, which of the following costs would be included in finished goods inventory?
a.neither variable nor fixed factory overhead cost
b.both variable and fixed factory overhead cost
c.only variable factory overhead cost
d.only fixed factory overhead cost
73.Under variable costing, which of the following costs would be included in finished goods inventory?
a.salary of salesperson
b.salary of vice-president of finance
c.wages of carpenters in a furniture factory
d.straight-line depreciation on factory equipment
74.Under variable costing, which of the following costs would notbe included in finished goods inventory?
a.wages of machine operator
b.steel costs for a machine tool manufacturer
c.salary of factory supervisor
d.electricity used by factory machinery
75.Which of the following would be included in the cost of a product manufactured according to absorption costing?
a.advertising expense
b.sales salaries
c.depreciation expense on factory building
d.office supplies costs
76.Which of the following would be included in the cost of a product manufactured according to variable costing?
a.sales commissions
b.office supply costs
c.interest expense
d.direct materials
77.On the variable costing income statement, the figure representing the difference between manufacturing marginand contribution margin is the:
a.fixed manufacturing costs
b.variable cost of goods sold
c.fixed selling and administrative expenses
d.variable selling and administrative expenses
78.In the variable costing income statement, deduction of variable selling and administrative expenses frommanufacturing margin yields:
a.differential margin
b.contribution margin
c.gross profit
d.marginal expenses
79.The amount of income under absorption costing will equal the amount of income under variable costing when unitsmanufactured:
a.exceed units sold
b.equal units sold
c.are less than units sold
d.are equal to or greater than units sold
80.The amount of income under absorption costing will be less than the amount of income under variable costing whenunits manufactured:
a.exceed units sold
b.equal units sold
c.are less than units sold
d.are equal to or greater than units sold
26. Sierra Company manufactures woven blankets and accounts for product costs using process costing. The
Sierra Company manufactures woven blankets and accounts for product costs using process costing. The following information is available regarding its May inventories. |
Beginning | Ending | |||||
Raw materials inventory | $ | 52,000 | $ | 106,000 | ||
Goods in process inventory | 414,000 | 531,000 | ||||
Finished goods inventory | 602,000 | 469,001 | ||||
The following additional information describes the company's production activities for May. |
| |||
Raw materials purchases (on credit) | $ | 280,000 | |
Factory payroll cost (paid in cash) | 1,556,000 | ||
Other overhead cost (Other Accounts credited) | 74,500 | ||
Materials used | |||
Direct | $ | 158,000 | |
Indirect | 68,000 | ||
Labor used | |||
Direct | $ | 790,000 | |
Indirect | 766,000 | ||
Overhead rate as a percent of direct labor | 115 | % | |
Sales (on credit) | $ | 3,500,000 |
Compute the cost of products transferred from production to finished goods and cost of goods sold. |
27. 1. How does philosophy influence curriculum workers? 2. In what way did each of the four major...
1. How does philosophy influence curriculum workers?
2. In what way did each of the four major philosophies influence U.S. education?
3. What are the differences between perennialism, essentialism, progressivism, and reconstructionism?
28. From the following list of selected items taken from the records of Bobcat Appliance Service as of...
From the following list of selected items taken from the records of Bobcat Appliance Service as of a specific date, identify those that would appear on the balance sheet:
1. Accounts Receivable
2. Cash
3. Common Stock
4. Fees Earned
5. Land
6. Supplies
7. Supplies Expense
8. Utilities Expense
9. Wages Expense
10. Wages Payable
29. Cedar Springs Company completed the following selected transactions during June 2014: June 1....
PR 7-2B Transactions for petty cash, cash short and over
Cedar Springs Company completed the following selected transactions during June 2014: June 1. Established a petty cash fund of $1,000.
12. The cash sales for the day, according to the cash register records, totaled $9,440.
The actual cash received from cash sales was $9,506.
30. Petty cash on hand was $46. Replenished the petty cash fund for the following disbursements, each evidenced by a petty cash receipt:
June 2. Store supplies, $375.
10. Express charges on merchandise purchased, $105 (Merchandise Inventory).
14. Office supplies, $85.
15. Office supplies, $90.
18. Postage stamps, $33 (Office Supplies).
20. Repair to fax, $100 (Miscellaneous Administrative Expense).
21. Repair to office door lock, $25 (Miscellaneous Administrative Expense).
22. Postage due on special delivery letter, $9 (Miscellaneous Administrative Expense).
28. Express charges on merchandise purchased, $110 (Merchandise Inventory).
30. The cash sales for the day, according to the cash register records, totaled $13,390. The actual cash received from cash sales was $13,350.
30. Increased the petty cash fund by $200.
Instructions
Journalize the transactions.
30. A. Variable costs are always relevant, and fixed costs are always irrelevant. Do you agree or disagr
A. Variable costs are always relevant, and fixed costs are always irrelevant. Do you agree or disagree? Why?
B. What is the Difference between Relevant Cost and Irrelevant Costs.
C. Companies should focus on financial measures of quality because these are the only measures of quality that can be linked to bottom-line performance.Ac€?? Do you agree or disagree? Explain.
D. Are there any other non-financial measures that companies should focus on?
31. Last year Ace charged $1,258,560 Depreciation on the Income Statement of Andrews. If early this y...
Last year Ace charged $1,258,560 Depreciation on the Income Statement of Andrews. If early this year Ace sold all its depreicable assets for their book value, the effect on Andrews's financial statements would be (all other items remaining equal): | ||||||||
Select: 1 | ||||||||
|
32. Beacon Signals Company maintains and repairs warning lights, such as those found on radio towers and
Beacon Signals Company maintains and repairs warning lights, such as those found on radio towers and lighthouses. Beacon Signals Company prepared the following end-ofperiod spreadsheet at December 31, 2019, the end of the fiscal year:
Beacon Signals Company
End-of-Period Spreadsheet
For the Year Ended December 31, 2019
Unadjusted Trial Balance Adjustments Adjusted Trial Balance
Account Title Dr. Cr. Dr. Cr. Dr. Cr.
Cash 13,000.00 13,000.00
Accounts Receivable 40,500.00 (a) 12,500.00 53,000.00
Prepaid Insurance 4,200.00 (b) 3,000.00 1,200.00
Supplies 3,000.00 (c) 2,250.00 750.00
Land 98,000.00 98,000.00
Building 500,000.00 500,000.00
Accumulated Depreciation-Building 255,300.00 (d) 9,000.00 264,300.00
Equipment 121,900.00 121,900.00
Accumulated Depreciation-Equipment 100,100.00 (e) 4,500.00 104,600.00
Accounts Payable 15,700.00 15,700.00
Salaries and Wages Payable (f) 4,900.00 4,900.00
Unearned Rent 2,100.00 (g) 1,300.00 800.00
Sarah Colin, Capital 238,100.00 238,100.00
Sarah Colin, Drawing 10,000.00 10,000.00
Fees Earned 388,700.00 (a) 12,500.00 401,200.00
Rent Revenue (g) 1,300.00 1,300.00
Salaries and Wages Expense 163,100.00 (f) 4,900.00 168,000.00
Advertising Expense 21,700.00 21,700.00
Utilities Expense 11,400.00 11,400.00
Depreciation Expense-Building (d) 9,000.00 9,000.00
Repairs Expense 8,850.00 8,850.00
Depreciation Expense-Equipment (e) 4,500.00 4,500.00
Insurance Expense (b) 3,000.00 3,000.00
Supplies Expense (c) 2,250.00 2,250.00
Miscellaneous Expense 4,350.00 4,350.00
1,000,000.00 1,000,000.00 37,450.00 37,450.00 1,030,900.00 1,030,900.00
Required:
4. Based upon the end-of-period spreadsheet, journalize the closing entries. Explanations should be omitted. If you are unsure of account titles, see the chart of accounts.
I have attached a picture of the income statement portion of the question which was already completed with the values as well
33. 21.3 Explain how end users develop, use, and control computer-based information systems. 1) Which of
21.3 Explain how end users develop, use, and control computer-based information systems.
1) Which of the following is not an appropriate task end users to perform?
A) performing statistical analyses
B) preparing schedules and lists
C) retrieving information from databases
D) updating database records
2) What is the basic function of a help desk?
A) control access to corporate data
B) provide technical maintenance and support
C) train end users and assist with application development
D) All of the above are basic functions of a help desk.
3) ________ refers to involving users in the development, control, and deployment of information systems.
A) Amateur user computing (AUC)
B) Competitive intra-organization systems development approach (CIOSDA)
C) End-user computing (EUC)
D) Novice information systems development (NISD)
4) Identify the system below that end users should not be allowed to develop.
A) a payroll processing program
B) a program that performs "what-if" statistical modeling
C) developing an application using prewritten software such as a spreadsheet or database system
D) preparing a schedule or list such as a depreciation schedule
5) Identify one of the primary risks associated with end-user computing below.
A) IS personnel will not have enough work to do if users develop their own systems.
B) Systems that have not been adequately tested may be implemented.
C) System costs may skyrocket.
D) System development time may increase substantially.
6) Which of the following about end-user computing is true?
A) System users know best what they need, so should be able to create their own applications.
B) End-users, while knowledgeable about their job, are not trained to create systems applications, and should not be allowed to do so.
C) It is inefficient and costly to ask the IS department to create basic applications that only a few users need to use.
D) In most companies, the IS department doesn't want end-users to create their own applications, for fear IS won't have enough work to do.
7) A second-line help desk operator would most likely
A) handle complicated queries requiring research.
B) provide callers with scripted answers.
C) use expert systems to quickly find answers.
D) None of the duties listed above pertain to second-line help desk personnel.
8) End-user computing is likely to result in a(n)
A) well tested system.
B) well documented system.
C) rapidly developed system.
D) efficient system.
9) Where is the responsibility for the development of end-user computing applications typically placed?
A) end users
B) help desk
C) Information Technology Services Department
D) programmers
10) Describe the purposes of a help desk.
11) Describe end-user computing and the advantages and risks involved.
34. CASE STUDY: MERRITT’S BAKERY In 1979, Larry and Bobbie Merritt bought The Cake Box, a small business
CASE STUDY:
MERRITT’S BAKERY
In 1979, Larry and Bobbie Merritt bought The Cake Box, a small business located in a tiny 450-foot store in Tulsa, Oklahoma. The couple were the only employees. “I would make cakes and Bobbie would come in and decorate them,” Larry recalls. Bobbie Merritt was already skilled in decorating cakes, whereas baking was a new occupation for Larry Merritt, who previously worked as a discount store manager. So, Larry spent hours pouring over baking books in the local library and testing recipes through trialand-error experimentation. “I threw away a lot of ingredients that first year,” he recalls.
Sales were initially slow. Then, a doughnut shop around the corner was put up for sale, and its owner made it possible for the Merritts to buy that business. They moved to the larger location and changed the company’s name to Merritt’s Bakery to reflect the broader variety of products sold. The Merritts hired their first two employees, who performed front-of-store sales and service. Over the next decade, Merritt’s Bakery’s physical space doubled and its revenues increased 13-fold. The company employed 20 people by the time it made its next move.
In 1993, Merritt’s Bakery moved to a 6,000-foot location across the street. The business became so popular that customers were lining up down the street to buy its freshbaked goods. “That looks like success to a lot of people, but that was failure,” says Bobbie Merritt. The problem was that the couple didn’t want to delegate production to employees, but they couldn’t produce their baked goods or decorate their carefully crafted cakes fast enough to keep up with demand. “We felt like failures because we had to work those 20 hours (per day),” she reflects.
At some point, the Merritts realized that they had to become business owners and managers rather than bakers. They devised a plan to grow the business and drew up an organizational structure that formalized roles and responsibilities. When a second Merritt’s Bakery store opened across town in 2001, each store was assigned a manager, a person in charge of baking production, another in charge of cake decorating and pastries, and someone responsible for sales. A third store opened a few years later. Larry worked on maintaining quality by training bakery staff at each store. “Because it is so difficult to find qualified bakers nowadays, I want to spend more time teaching and developing our products,” he said at the time.
Christian Merritt, one of Larry and Bobbie’s sons, joined the business in 2000 and now runs the business. An engineer by training with experience in the telecommunications industry, Christian soon developed flowcharts that describe precise procedures for most work activities, ranging from simple store-front tasks (cashiering) to unusual events such as a power outage. These documents standardized work activities to maintain quality with less reliance on direct supervision. Christian also introduced computer systems to pool information across stores about how much inventory exists, which products are selling quickly, and how much demand exists for Merritt’s famous custom cakes. The information improved decision making about production, staffing, and purchasing without having to directly contact or manage each store as closely.
In late 2007, Merritt’s Bakery opened a dedicated production center near the original store and moved all production staff into the building, affectionately called “the Fort.” The centralized production facility reduced costs by removing duplication of staff and equipment, provided more consistent quality, and allowed the stores to have more front store space for customers.
Merritt’s Bakery also refined its training programs, from the initial orientation session to a series for modules on specific skills. For example, front-of-store staff complete a series of clinics that add up to 20 hours of training. The company also introduced special selection processes so people with the right personality and skills are hired into these jobs. Employees at Merritt’s production facility receive decorator training through a graduated program over a longer time. One or two managers at the production site closely coach up to five new hires.
Today, Merritt’s Bakery employs more than 80 people, including production managers, store managers, and a marketing director. Two-thirds of the business is in the creation of cakes for birthdays, weddings, and other events, but the company also has three busy and popular stores across Tulsa. “We’re just now getting the pieces in place to start to treat Merritt’s Bakery like a business, with a lot of parts that we manage from a distance,” says Christian Merritt. “We’re present but detached; we have our hands in a lot of things, but it’s in managing stores instead of operating them.”
Discussion Questions
1. How have the division and coordination of labor evolved at Merritt’s Bakery from its beginnings to today?
2. Describe how span of control, centralization, and formalization have changed at Merritt’s Bakery over the years. Is the company’s organizational structure today more mechanistic or organic? Are these three organizational structure elements well suited to the company in their current form? Why or why not?
3. What form of departmentalization currently exists at Merritt’s Bakery? Would you recommend this form of departmentalization to this company? Why or why not?
35. Suppose the following data were taken from the 2017 and 2016 financial statements of American...
Suppose the following data were taken from the 2017 and 2016 financial statements of American Eagle Outfitters. (All numbers, including share data, are in thousands.)
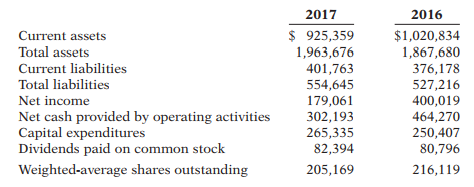
Instructions Perform each of the following.
(a) Calculate the current ratio for each year.
(b) Calculate earnings per share for each year.
(c) Calculate the debt to assets ratio for each year.
(d) Calculate the free cash flow for each year.
(e) Discuss American Eagle’s solvency in 2017 versus 2016.
(f) Discuss American Eagle’s ability to finance its investment activities with net cash provided by operating activities, and how any deficiency would be met.