
ACCT 617: Applications of Contract Theory in Accounting...
31. Val's Hair Emporium operates a hair salon. Its unadjusted trial balance as of December 31, 2013, ...
HELP! if you could explain some of these red ones that would be awesome!!
Val's Hair Emporium operates a hair salon. Its unadjusted trial balance as of December 31, 2013, follows along with information about selected accounts Account Names Debit Further Information 3,800 Cash As reported on December 31 bank state ment Supplies 4300 Based on count, only $1,300 of supplies still exist. This amount was paid November 1 for rent through the end of January. 1,500 This represents the total amount of bills received for utilities through December 15. Val estimates that the company has received $450 of utility services through December 31 for which it has not yet been billed Stylists have not yet been paid $150 for their work on December 31 The company has paid last year's income taxes but not this year's taxes 2,000 This amount was contributed to the company in prior years 900 This is the balance reported at the end of last year. 75,800 Customers pay cash when they receive services. 6000 Prepaid Rent Accounts Payable Wages Payable ncome Tax Payable Contributed Capita Retained Earnings Service Revenue Wages Expense 29,100 This is the cost of stylist wages through December 30 This is the cost of utilities through December 15. This year's rent was $2,000 per month This is the cost of supplies used through November 30 The company has an average tax rate of 30%. Utilities Expense 12,200 Rent Expense 20,000 Supplies 4,800 nSe ncome Tax Expense 80,200 80,200 Totals
32. Dozier Company produced and sold 1,000 units during its first month of operations. It reported th...
Dozier Company produced and sold 1,000 units during its first month of operations. It reported the following costs and expenses for the month: Direct materials Direct labor Variable manufacturing overhead Fixed manufacturing overhead Total manufacturing overhead Variable selling expense Fixed selling expense Total selling expense Variable administrative expense Fixed administrative expense Total administrative expense $83,000 $ 42,000 s 20,600 32,200 $ 52,800 $14,800 23,600 38,400 $ 5,400 27,800 $33,200 Required 1. With respect to cost classifications for preparing financial statements a. What is the total product cost? b. What is the total period cost? 2. With respect to cost classifications for assigning costs to cost objects a. What is total direct manufacturing cost? b. What is the total indirect manufacturing cost? 3. With respect to cost classifications for manufacturers a. What is the total manufacturing cost? b. What is the total nonmanufacturing cost? C. What is the total conversion cost and prime cost? 4. With respect to cost classifications for predicting cost behavior: a. What is the total variable manufacturing cost? b. What is the total fixed cost for the company as a whole? C. What is the variable cost per unit produced and sold? 5. With respect to cost classifications for decision making a. If Dozier had produced 1,001 units instead of 1,000 units, how much incremental manufacturing cost would it have incurred to make the additional unit?
33. answer and show your solution Problem 1-3 (IAA) Manchester Company provided the following informatio
December 31, 2020: Income taxes withheld from employees 900,000 Cash balance at First State Bank 2.500.000 Cash overdraft at Harbor Bank 1,300,000 Accounts receivable with credit balance 750,000 Estimated expenses of meeting warranties on merchandise previously sold 500,000 Estimated damages as a result of unsatisfactory 1,500,000 performance on a contract 3,000,000 Accounts payable Deferred serial bonds, issued at par and bearing interest at 12%, payable in semiannual installment of P500,000 due April 1 and October 1 of each year, the last bond to be paid on October 1, 2026. Interest is also paid semiannually. 5.000.000 Stock dividend payable 2,000,000 Required: S.IN Compute the total current liabilitics on December 31, 2020. Problem 14 (AICPA Adapted) Multiple Company provided the following information on December 31, 2020: Accounts payable after deducting debit balances in suppliers' accounts of P100,000 500,000 Accrued liabilities 50,000 Note payable-due March 31, 2021 1,000,000 Note payable-due May 1, 2021 800,000 Bonds payable-due December 31, 2022 2,000,000 On March 1, 2021 before the 2020 financial statements were issued, the note payable of P1,000,000 was replaced by an 18-month note for the same amount. The entity is considering similar action on the P800,000 note due on May 1, 2021. The financial statements were issued on March 31, 2021. Required: 1. Compute total current liabilities. 2. Compute total noncurrent liabilities. 16
34. 11.The Transaction Processing System includes all of the following cycles except a. the revenue...
11.The Transaction Processing System includes all of the following cycles except
a. | the revenue cycle |
b. | the administrative cycle |
c. | the expenditure cycle |
d. | the conversion cycle |
12.The primary input to the Transaction Processing System is
a. | a financial transaction |
b. | an accounting record |
c. | an accounting report |
d. | a nonfinancial transaction |
13.When designing the data collection activity, which type of data should be avoided?
a. | data that is relevant |
b. | data that is efficient |
c. | data that is redundant |
d. | data that is accurate |
14.The most basic element of useful data in the database is
a. | the record |
b. | the key |
c. | the file |
d. | the attribute |
15.In a database, a complete set of attributes for a single occurrence of an entity class is called
a. | a key |
b. | a file |
c. | a record |
d. | a character |
16.Effective information has all of the following characteristics except
a. | relevance |
b. | completeness |
c. | summarization |
d. | structure |
17.Database management tasks do not include
a. | summarization |
b. | storage |
c. | retrieval |
d. | deletion |
18.The author distinguishes between the Accounting Information System and the management Information System based on
a. | whether the transactions are financial or nonfinancial |
b. | whether discretionary or nondiscretionary reports are prepared |
c. | the end users of the reports |
d. | the organizational structure of the business |
19.Which activity is not part of the finance function?
a. | cash receipts |
b. | portfolio management |
c. | credit |
d. | general ledger |
20.Market research and advertising are part of which business function?
a. | materials management |
b. | finance |
c. | marketing |
d. | production |
35. An analysis of the transactions made by Foley & Co., a certified public accounting firm, for ...
An analysis of the transactions made by Foley & Co., a certified public accounting firm, for the month of August is shown below. Each increase and decrease in stockholders' equity is explained.
a. Describe each transaction that occurred for the month (Provide the explanation for each transaction)
b. Determine how much stockholders' equity increased for the month.
ncome for the month.
Show transcribed image text An analysis of the transactions made by Foley & Co., a certified public accounting firm, for the month of August is shown below. Each increase and Stockholders' Equity Assets Liabilities Retained Earnings Accounts Accounts Common Supplies Equipment Receivable Payable Stock Cash Rev. Exp. Div. $15,000 $15,000 2 -2,000 $5,000 $3,000 $750 750 4 4,900 $4,500 $9,400 Service Revenue 1,500 1,500 -2.000 $2,000 850 $850 Rent Expense 450 450 9 -3,900 -3,900 Sal /Wages Expense 500 10 500 Utilities Expense
36. I need the solution manual for the 9th edition of Systems Understanding Aid. If someone has Docum...
I need the solution manual for the 9th edition of Systems Understanding Aid. If someone has Document 25, then that would be a huge help. I have been using Transaction List B which is the green one. As the pictures show, my unadjusted trail balance does not equal.
37. 5.32 The quality control manager of Marilyn’s Cookies is inspecting a batch of chocolate-chip...
5.32 The quality control manager of Marilyn’s Cookies is inspecting a batch of chocolate-chip cookies that has just been baked. If the production process is in control, the mean number of chip parts per cookie is 6.0. What is the probability that in any particular cookie being inspected a. fewer than five chip parts will be found? b. exactly five chip parts will be found? c. five or more chip parts will be found? d. either four or five chip parts will be found? 5.33 Refer to Problem 5.32. How many cookies in a batch of 100 should the manager expect to discard if company policy requires that all chocolate-chip cookies sold have at least four chocolate-chip parts?
38. The ledger of Armour Lake Lumber Supply on July 31, 2017, includes the selected accounts below...
The ledger of Armour Lake Lumber Supply on July 31, 2017, includes the selected accounts below before adjusting entries have been prepared.

An analysis of the company’s accounts shows the following.
1. The investment in the notes receivable earns interest at a rate of 6% per year.
2. Supplies on hand at the end of the month totaled $18,600.
3. The balance in Prepaid Rent represents 4 months of rent costs.
4. Employees were owed $3,100 related to unpaid salaries and wages.
5. Depreciation on buildings is $6,000 per year.
6. During the month, the company satisfied obligations worth $4,700 related to the Unearned Services Revenue.
7. Unpaid maintenance and repairs costs were $2,300.
39. The May 31, 2009 trial balance for Lucena Bacalso Surveyors is presented as follows: Lucena...
The May 31, 2009 trial balance for Lucena Bacalso Surveyors is presented as follows:
Lucena Bacalso Surveyors
Trial Balance
May 31, 2009
Cash P 210,000
Accounts Receivable 930,000
Prepaid Advertising 360,000
Engineering Supplies 270,000
Survey Equipment 1,890,000
Accum. Depreciation-Survey Equipment P 640,000
Accounts Payable 190,000
Unearned Survey Revenues 120,000
Notes Payable 500,000
Bacalso, Capital 1,120,000
Bacalso, Withdrawals 700,000
Survey Revenues 6,510,000
Salaries Expense 3,270,000
Rent Expense 960,000
Insurance Expense 250,000
Utilities Expense 160,000
Miscellaneous Expense 80,000_________________________
Total P9,080,000 P9,080,000
_________________________________
The following information pertaining to the year-end adjustment is available:
a. The P360, 000 prepaid advertising represents expenditure made on November 1, 2008 for monthly advertising over the next 18 months.
b. A count of the engineering supplies at May 31, 2009 amounted to P90, 000.
c. Depreciation on the surveying equipment amounted to P160, 000.
d. One-third of the unearned survey revenues has been earned at year-end.
e. At year-end, salaries in the amount of P140, 000 have accrued.
f. Interest of P60, 000 on the notes payable has accrued at year-end.
Required: Prepare the adjustments on the worksheet and complete the worksheet.
40. On December 1, 2017, Devine Distributing Company had the following account balances. During...
On December 1, 2017, Devine Distributing Company had the following account balances.
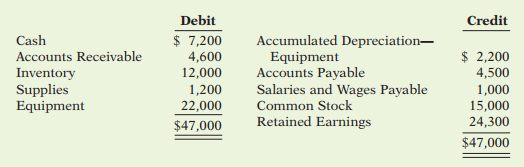
During December, the company completed the following summary transactions.
Dec. 6 Paid $1,600 for salaries due employees, of which $600 is for December and $1,000 is for November salaries payable.
8 Received $1,900 cash from customers in payment of account (no discount allowed).
10 Sold merchandise for cash $6,300. The cost of the merchandise sold was $4,100.
13 Purchased merchandise on account from Hecht Co. $9,000, terms 2/10, n/30.
15 Purchased supplies for cash $2,000.
18 Sold merchandise on account $12,000, terms 3/10, n/30. The cost of the merchandise sold was $8,000.
20 Paid salaries $1,800.
23 Paid Hecht Co. in full, less discount.
27 Received collections in full, less discounts, from customers billed on December 18
Adjustment data:
1. Accrued salaries payable $800.
2. Depreciation $200 per month.
3. Supplies on hand $1,500.
4. Income tax due and unpaid at December 31 is $200. Instructions
(a) Journalize the December transactions using a perpetual inventory system.
(b) Enter the December 1 balances in the ledger T-accounts and post the December transactions. Use Cost of Goods Sold, Depreciation Expense, Salaries and Wages Expense, Sales Revenue, Sales Discounts, Supplies Expense, Income Tax Expense, and Income Taxes Payable.
(c) Journalize and post adjusting entries.
(d) Prepare an adjusted trial balance.
(e) Prepare an income statement and a retained earnings statement for December and a classified balance sheet at December 31.
41. Selected worksheet data for Woodny Company are presented below.
Selected worksheet data for Woodny Company are presented below.
Instructions
(a) Fill in the missing amounts.
(b) Prepare the adjusting entries that weremade.

42. 31.Which of the following is (are) the proper time period(s) to record the effects of a change in...
31.Which of the following is (are) the proper time period(s) to record the effects of a change in accounting estimate?
a.Current period and prospectively
b.Current period and retrospectively
c.Retrospectively only
d.Current period only
32.When a company decides to switch from the double-declining balance method to the straight-line method, this change should be handled as a a. change in accounting principle.
b.change in accounting estimate.
c.prior period adjustment.
d.correction of an error.
33.The estimated life of a building that has been depreciated 30 years of an originally estimated life of 50 years has been revised to a remaining life of 10 years. Based on this information, the accountant should
a.continue to depreciate the building over the original 50-year life.
b.depreciate the remaining book value over the remaining life of the asset.
c.adjust accumulated depreciation to its appropriate balance, through net income, based on a 40-year life, and then depreciate the adjusted book value as though the estimated life had always been 40 years.
d.adjust accumulated depreciation to its appropriate balance through retained earnings, based on a 40-year life, and then depreciate the adjusted book value as though the estimated life had always been 40 years.
34.Which of the following statements is correct?
a.Changes in accounting principle are always handled in the current or prospective period.
b.Prior statements should be restated for changes in accounting estimates.
c.A change from expensing certain costs to capitalizing these costs due to a change in the period benefited, should be handled as a change in accounting estimate.
d.Correction of an error related to a prior period should be considered as an adjustment to current year net income.
35.Which of the following describes a change in reporting entity?
a.A company acquires a subsidiary that is to be accounted for as a purchase.
b.A manufacturing company expands its market from regional to nationwide.
c.A company divests itself of a European branch sales office.
d.Changing the companies included in combined financial statements.
36.Presenting consolidated financial statements this year when statements of individual companies were presented last year is a. a correction of an error.
b.an accounting change that should be reported prospectively.
c.an accounting change that should be reported by restating the financial statements of all prior periods presented.
d.not an accounting change.
37.An example of a correction of an error in previously issued financial statements is a change
a.from the FIFO method of inventory valuation to the LIFO method.
b.in the service life of plant assets, based on changes in the economic environment.
c.from the cash basis of accounting to the accrual basis of accounting.
d.in the tax assessment related to a prior period.
38.Counterbalancing errors do not include
a.errors that correct themselves in two years.
b.errors that correct themselves in three years.
c.an understatement of purchases.
d.an overstatement of unearned revenue.
39.A company using a perpetual inventory system neglected to record a purchase of merchandise on account at year end. This merchandise was omitted from the year-end physical count. How will these errors affect assets, liabilities, and stockholders' equity at year end and net income for the year?
Assets Liabilities Stockholders' Equity Net Income a. No effect Understate Overstate Overstate.
b.No effect Overstate Understate Understate.
c.Understate Understate No effect No effect.
d.Understate No effect Understate Understate.
40.If, at the end of a period, a company erroneously excluded some goods from its ending inventory and also erroneously did not record the purchase of these goods in its accounting records, these errors would cause
a.the ending inventory and retained earnings to be understated.
b.the ending inventory, cost of goods sold, and retained earnings to be understated.
c.no effect on net income, working capital, and retained earnings.
d.cost of goods sold and net income to be understated.
43. HELP ME WITH THIS ADJUSTING ENTRY. PLS.
what would be the entry for this " the notes receivable were accepted from several customers. the notes were issued on sept 1, 2006 and will be settled together with a 20% interest on may 31, 2007"it's about adjusting entry. im just confused whether i would divide it by 9(sept-may) or 12(1year). thanks for the help if ever. :))
44. Finley Company End-of-Period Spreadsheet For the Year Ended December 31 Adjusted Trial Balanc...
Finley Company | ||||||
| Income Statement | Balance Sheet | ||||
Account Title | Debit | Credit | Debit | Credit | Debit | Credit |
Cash | 48,000 | 48,000 | ||||
Accounts Receivable | 18,000 | 18,000 | ||||
Supplies | 6,000 | 6,000 | ||||
Equipment | 57,000 | 57,000 | ||||
Accumulated Depreciation | 18,000 | 18,000 | ||||
Accounts Payable | 25,000 | 25,000 | ||||
Wages Payable | 6,000 | 6,000 | ||||
Common Stock | 30,000 | 30,000 | ||||
Retained Earnings | 3,000 | 3,000 | ||||
Dividends | 3,000 | 3,000 | ||||
Fees Earned | 155,000 | 155,000 | ||||
Wages Expense | 63,000 | 63,000 | ||||
Rent Expense | 27,000 | 27,000 | ||||
Depreciation Expense | 15,000 |
| 15,000 | |||
Totals | 237,000 | 237,000 | 105,000 | 155,000 | 132,000 | 82,000 |
Net Income (Loss) | 50,000 |
|
| 50,000 | ||
155,000 | 155,000 | 132,000 | 132,000 | |||
The entry to close the dividends account would be
a. debit Dividends, $3,000; credit Retained Earnings, $3,000
b. debit Dividends, $12,000; credit Retained Earnings, $12,000
c. debit Retained Earnings, $3,000; credit Dividends, $3,000
d. debit Retained Earnings, $12,000; credit Dividends, $12,000
45. 9.1 Questions 1) ________ is the logical integration of techniques to gather and report data for...
9.1 Questions
1) ________ is the logical integration of techniques to gather and report data for planning and control decisions and to evaluate performance.
A) An internal control system
B) A quality control system
C) A financial reporting system
D) A management control system
2) A management control system includes the techniques to gather and use information to ________.
A) motivate employee behavior
B) evaluate performance
C) make planning and control decisions
D) all of the above
3) Which of the following is NOT a characteristic of a management control system?
A) A management control system aids and coordinates the process of decision making.
B) A management control system encourages the use of only short-term goals.
C) A management control system motivates individuals throughout the organization to act in concert.
D) A management control system measures and evaluates performance.
4) What is the first step in designing a management control system?
A) evaluating management's performance
B) establishing organizational goals
C) preparing financial statements
D) differentiating between profit centers and cost centers
5) What is the first and most basic component in a management control system?
A) the organization's long-range budget
B) the organization's goals
C) the stockholders' goals
D) the manager's personal desires
6) ________ are characteristics or attributes that managers must achieve to drive the organization toward its goals.
A) Nonfinancial performance measures
B) Targets
C) Key success factors
D) Objectives
7) Which of the following statements about performance measures is FALSE?
A) Organizational goals without performance measures do not motivate managers.
B) Every performance measure used to evaluate employees should be consistent with organizational goals.
C) An ideal management control system should include at least one performance measure related to every goal.
D) Performance measures become more specific at higher levels of the organization.
8) A hotel has the following organizational goal: Increase customer satisfaction of overnight guests by 50%. Which is the best performance measure of the organizational goal?
A) number of new employees trained
B) turnover rate of hotel employees
C) overall rating on guest satisfaction survey
D) percent of guests paying by credit card
9) A management control system is a logical integration of techniques to gather and report data and to evaluate performance.
10) The purpose of performance measures is to set direction and to motivate managers.
11) The first and most basic component in a management control system is the employee's goals.
12) In the management control system, feedback and learning affect all elements of the system.
13) Measures of performance do not have to be consistent with organizational goals.
46. Single plantwide factory overhead rate Salty Sensations Snacks Company manufactures three types...
Single plantwide factory overhead rate
Salty Sensations Snacks Company manufactures three types of snack foods: tortilla chips, potato chips, and pretzels. The company has budgeted the following costs for the upcoming period:
Factory depreciation | $ 31,360 |
Indirect labor | 78,400 |
Factory electricity | 7,840 |
Indirect materials | 35,400 |
Selling expenses | 25,000 |
Administrative expenses | 18,000 |
Total costs | $196,000 |
Factory overhead is allocated to the three products on the basis of processing hours. The products had the following production budget and processing hours per case:
Budgeted Volume (Cases) | Processing Hours per Case | |
Tortilla chips | 4,000 | 0.20 |
Potato chips | 5,000 | 0.15 |
Pretzels | 2,500 | 0.40 |
Total 11,500
a. Determine the single plantwide factory overhead rate.
b. Use the factory overhead rate in (a) to determine the amount of total and per-case factory overhead allocated to each of the three products under generally accepted accounting principles.
47. Sales mix, two products. The Goldman Company retails two product
Sales mix, two products. The Goldman Company retails two products: a standard and a deluxe version of a luggage carrier. The budgeted income statement for next period is as follows:
1. Compute the breakeven point in units assuming that the planned sales mix is attained.
2. Compute the breakeven point in units (a) if only standard carriers are sold and (b) if only deluxe carriers are sold.
3. Suppose 200,000 units are sold but only 20,000 of them are deluxe. Compute the operating income. Compute the breakeven point in units. Compare your answer with the answer to requirement 1. What the major lesson of thisproblem?

48. Identify the item below that would cause the trial balance to not balance. A $1,000 collection of...
Identify the item below that would cause the trial balance to not balance.
A $1,000 collection of an account receivable was erroneously posted as a debit to Accounts Receivable and a credit to Cash.
The purchase of office supplies on account for $3,250 was erroneously recorded in the journal as $2,350 debit to Office Supplies and credit to Accounts Payable.
A $50 cash receipt for the performance of a service was not recorded at all.
The purchase of office equipment for $1,200 was posted as a debit to Office Supplies and a credit to Cash for $1,200.
The cash payment of a $750 account payable was posted as a debit to Accounts Payable and a debit to Cash for $750.
49. What is the finished good in this one?
The Devon Motor Company produces motorcycles. During April, the company purchased 8,000 batteries at a cost of $10 per battery. Devon withdrew 7,600 batteries from the storeroom during the month. Of these, 100 were used to replace batteries in motorcycles used by the company's traveling sales staff....
50. 21. If a firm uses variable costing, fixed manufacturing overhead will be included a. only on the...
21. If a firm uses variable costing, fixed manufacturing overhead will be included
a. only on the balance sheet.
b. only on the income statement.
c. on both the balance sheet and income statement.
d. on neither the balance sheet nor income statement.
22. Under variable costing,
a. all product costs are variable.
b. all period costs are variable.
c. all product costs are fixed.
d. product costs are both fixed and variable.
23. How will a favorable volume variance affect net income under each of the following methods?
Absorption Variable
a. reduce no effect
b. reduce increase
c. increase no effect
d. increase reduce
24. Variable costing considers which of the following to be product costs?
Fixed Fixed Variable Variable
Mfg. Costs Selling & Adm. Mfg. Costs Selling & Adm.
a. yes no yes no
b. yes no yes yes
c. no no yes yes
d. no no yes no
25. The variable costing format is often more useful to managers than the absorption costing format because
a. costs are classified by their behavior.
b. costs are always lower.
c. it is required for external reporting.
d. it justifies higher product prices.
26. The difference between the reported income under absorption and variable costing is attributable to the difference in the
a. income statement formats.
b. treatment of fixed manufacturing overhead.
c. treatment of variable manufacturing overhead.
d. treatment of variable selling, general, and administrative expenses.
27. Which of the following costs will vary directly with the level of production?
a. total manufacturing costs
b. total period costs
c. variable period costs
d. variable product costs
28. On the variable costing income statement, the difference between the “contribution margin” and “income before income taxes” is equal to
a. the total variable costs.
b. the Cost of Goods Sold.
c. total fixed costs.
d. the gross margin.
29. For financial reporting to the IRS and other external users, manufacturing overhead costs are
a. deducted in the period that they are incurred.
b. inventoried until the related products are sold.
c. treated like period costs.
d. inventoried until the related products have been completed.
30. In the application of “variable costing” as a cost-allocation process in manufacturing,
a. variable direct costs are treated as period costs.
b. nonvariable indirect manufacturing costs are treated as product costs.
c. variable indirect manufacturing costs are treated as product costs.
d. nonvariable direct costs are treated as product costs.